Social Media’s Impact on Law Enforcement and Judicial Processes: How Does Social Midi Effect Rule Of Law
Social media has fundamentally altered the landscape of law enforcement and judicial processes, presenting both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges. The sheer volume of data generated online, coupled with its accessibility, has revolutionized investigative techniques while simultaneously raising complex legal and ethical questions regarding evidence admissibility and potential biases.
Social media evidence plays a crucial role in modern investigations and trials. Its use ranges from identifying suspects and corroborating witness testimonies to uncovering crucial pieces of evidence previously inaccessible. However, the inherent nature of social media data necessitates careful consideration of its reliability and legal standing.
Social Media Evidence in Investigations and Trials
The use of social media evidence in investigations and trials presents both opportunities and challenges. Its value lies in its potential to provide direct insights into a suspect’s behavior, associations, and intentions. Conversely, challenges arise from the potential for manipulation, context misinterpretation, and questions of authenticity. The following table illustrates some key aspects:
| Evidence Type | Reliability Challenges | Legal Admissibility | Case Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photos/Videos | Potential for manipulation (e.g., editing, deepfakes), lack of verifiable metadata, context may be unclear. | Generally admissible if authenticated and relevant, but subject to challenges regarding authenticity and chain of custody. | Numerous cases involve social media photos/videos used to prove location, identity, or events, often facing challenges in proving authenticity. |
| Posts/Messages | Contextual understanding is crucial; messages can be easily misinterpreted or taken out of context. Deletion or editing of posts raises concerns. | Admissibility depends on authentication, relevance, and the absence of undue prejudice. Privacy concerns can also impact admissibility. | Cases involving online threats, harassment, or hate speech often rely on social media posts as evidence, with admissibility subject to rigorous scrutiny. |
| Location Data | Accuracy can be affected by network limitations or user settings. Privacy concerns are significant. | Admissible if obtained legally and relevant to the case. Warrants are usually required for accessing location data. | Cases involving stalking, kidnapping, or other crimes where location data can establish a suspect’s presence at a crime scene. |
Potential for Bias in Social Media Evidence
The use of social media evidence carries a significant risk of bias. Algorithms used to collect and analyze social media data may reflect existing societal biases, leading to disproportionate targeting of certain groups. Furthermore, the subjective interpretation of social media content by investigators and jurors can introduce further bias into the judicial process. For example, a seemingly innocuous post might be misinterpreted out of context, prejudicing the perception of a suspect. The lack of diverse perspectives in interpreting online interactions can amplify this bias.
Challenges in Monitoring and Regulating Online Criminal Activity
Law enforcement faces numerous challenges in monitoring and regulating online criminal activity. The sheer volume of data, the anonymity afforded by online platforms, and the cross-border nature of the internet make it difficult to track and prosecute offenders effectively. The rapid evolution of technology and the emergence of new platforms also present ongoing challenges. Resources are often limited, requiring careful prioritization of investigations. Furthermore, balancing the need for security with the protection of individual privacy rights presents a complex legal and ethical dilemma. International cooperation is often essential to effectively investigate crimes that transcend national borders.
Social Media and Activism Related to Legal Issues

Social media platforms have fundamentally altered the landscape of legal activism, providing unprecedented opportunities for individuals and groups to mobilize support, raise awareness, and advocate for legal reforms. The speed and reach of these platforms allow for rapid dissemination of information, fostering collective action around legal issues that might otherwise remain marginalized. This section will explore how social media campaigns have influenced legal change and the effectiveness of this approach.
Social media’s impact on legal activism is multifaceted. It allows for the rapid mobilization of supporters, bypassing traditional media gatekeepers and directly engaging with the public. This direct engagement fosters a sense of community and shared purpose, empowering individuals to participate in legal challenges and reforms in ways previously unimaginable. Furthermore, the ability to share visual content, personal stories, and easily digestible information amplifies the impact of activism, making complex legal issues more accessible to a wider audience.
Examples of Social Media Campaigns for Legal Reform
Several successful social media campaigns have directly influenced legal reforms. The #MeToo movement, for instance, leveraged social media to expose widespread sexual harassment and assault, prompting significant shifts in legal and societal attitudes towards these issues. Similarly, the Black Lives Matter movement effectively used social media to highlight police brutality and racial injustice, leading to increased public awareness and calls for legal reforms related to policing practices and accountability. These campaigns demonstrate the power of social media to amplify marginalized voices and create a powerful collective demand for change.
Effectiveness of Social Media in Mobilizing Public Support for Legal Causes, How does social midi effect rule of law
Social media’s effectiveness in mobilizing public support stems from its ability to create viral campaigns, fostering widespread awareness and engagement. The use of hashtags, trending topics, and targeted advertising allows activists to reach large and specific audiences. Moreover, the interactive nature of social media facilitates the creation of online communities, strengthening solidarity among supporters and increasing the pressure on lawmakers and institutions to address legal issues. The immediate feedback loops provided by social media platforms also enable activists to gauge public sentiment and adapt their strategies accordingly, leading to more effective campaigns. However, it is important to acknowledge that social media’s reach is not universally equitable, and some populations may remain underrepresented or excluded from these online movements.
Case Study: Social Media and Awareness of Criminal Justice Reform
The campaign for criminal justice reform, particularly concerning mass incarceration and sentencing disparities, has effectively utilized social media. Organizations like the Sentencing Project have leveraged platforms like Twitter and Facebook to share data, personal stories of individuals affected by the justice system, and information about pending legislation. These efforts have helped to raise awareness about the disproportionate impact of incarceration on marginalized communities and the need for systemic changes. The use of infographics, videos, and personal narratives has made complex statistical data more accessible and emotionally resonant, contributing to a broader public understanding and increased support for reform efforts. The resulting public pressure has influenced legislative debates and contributed to the passage of certain criminal justice reform bills at both state and federal levels.
Social Media, Misinformation, and the Rule of Law
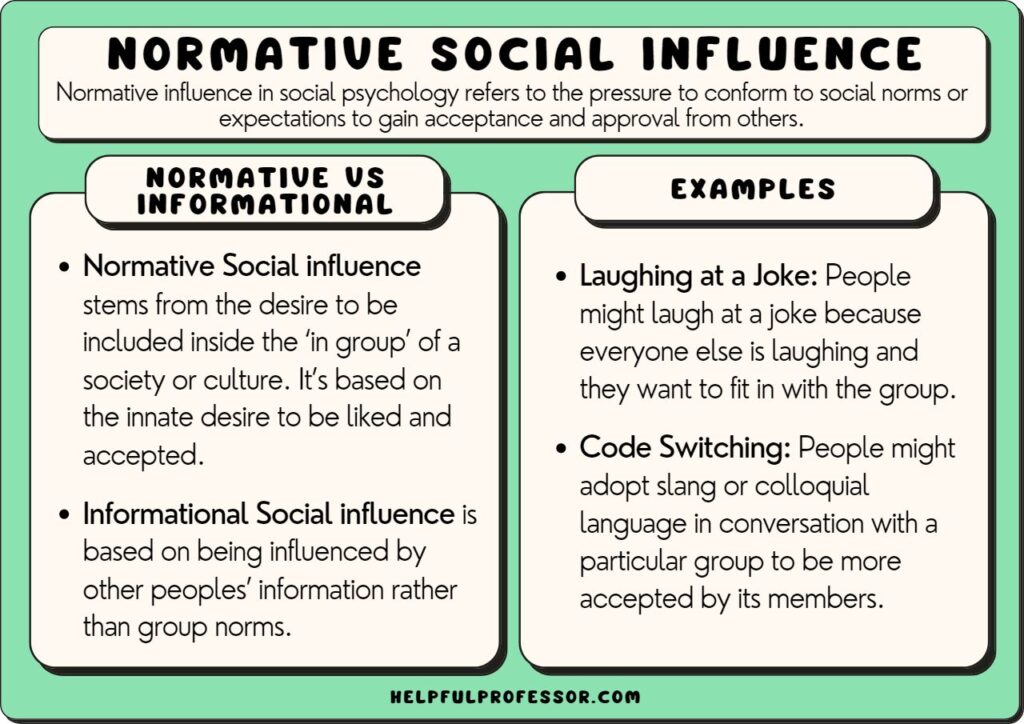
The pervasive nature of social media has created a fertile ground for the rapid dissemination of misinformation, significantly impacting public perception of legal institutions and the rule of law itself. The ease with which false or misleading information can be shared and amplified online poses a serious threat to the fair and effective functioning of the justice system. This section will explore the ways in which misinformation undermines public trust, the challenges in combating its spread, and strategies for mitigating its harmful effects.
Misinformation’s Erosion of Public Trust in Legal Institutions
The spread of misinformation regarding legal cases, court proceedings, and the actions of legal professionals can severely damage public trust. False narratives surrounding high-profile trials, for instance, can sway public opinion before a verdict is even reached, potentially influencing jury selection and creating an environment of distrust in the judicial process. Similarly, fabricated stories about police misconduct or judicial corruption, amplified through social media algorithms, can fuel widespread cynicism and erode confidence in law enforcement and the courts. This erosion of trust can lead to decreased participation in civic processes, reduced willingness to cooperate with law enforcement, and ultimately, a weakening of the rule of law. The lack of critical analysis and the tendency to accept information at face value, particularly within echo chambers, exacerbates the problem. For example, the rapid spread of unsubstantiated claims about election fraud following major elections has demonstrably shaken public faith in democratic institutions and the integrity of the electoral process, impacting the acceptance of legal rulings and outcomes.
Challenges in Combating the Spread of Legal Misinformation
Combating the spread of misinformation related to legal matters presents significant challenges. The sheer volume of information shared online, coupled with the speed at which it circulates, makes real-time fact-checking and correction extremely difficult. The decentralized nature of social media platforms makes it hard to identify and remove false content effectively. Furthermore, sophisticated disinformation campaigns often utilize techniques designed to evade detection, including the creation of fake accounts and the manipulation of algorithms. Identifying the source of misinformation and holding those responsible accountable is also a complex undertaking, often requiring extensive investigation and legal action. The global reach of social media further complicates efforts, as legal frameworks and enforcement mechanisms vary across countries. Finally, combating misinformation requires addressing underlying issues of media literacy and critical thinking skills within the population.
Strategies for Mitigating the Impact of Misinformation on the Rule of Law
Addressing the problem of misinformation requires a multi-pronged approach. Effective strategies must involve collaboration between governments, social media platforms, media organizations, and educational institutions.
- Improved Media Literacy Education: Investing in comprehensive media literacy programs at all levels of education is crucial. These programs should equip individuals with the skills to critically evaluate information sources, identify biases, and recognize disinformation tactics.
- Enhanced Fact-Checking and Verification Initiatives: Support for independent fact-checking organizations and the development of innovative tools for automated detection of misinformation are essential. These initiatives should focus on legal and judicial matters specifically.
- Increased Transparency and Accountability from Social Media Platforms: Social media companies should be held accountable for the content shared on their platforms. This includes implementing stricter policies on the spread of misinformation and taking proactive steps to remove false or misleading content.
- Strengthened Legal Frameworks: Governments need to develop and enforce laws that address the intentional spread of misinformation, while protecting freedom of speech. This could involve measures to hold individuals and organizations accountable for the dissemination of demonstrably false information.
- Proactive Communication from Legal Institutions: Legal institutions themselves should actively engage in public communication efforts to counter misinformation and build trust. This could involve transparently sharing information about court proceedings and law enforcement activities.
Regulation of Social Media and its Relation to the Rule of Law

The regulation of social media presents a complex challenge, balancing the fundamental right to free speech with the need to protect individuals and society from harmful content. This delicate equilibrium necessitates careful consideration of legal frameworks and their effectiveness in addressing the unique issues posed by these platforms. The approaches taken by various jurisdictions differ significantly, reflecting varying cultural perspectives and legal traditions.
Legal frameworks governing social media content grapple with defining and addressing a wide spectrum of issues, from hate speech and misinformation to privacy violations and incitement to violence. These frameworks often intersect with existing laws concerning defamation, copyright infringement, and criminal activity, but the sheer scale and speed of information dissemination on social media platforms necessitate specific considerations. The impact on free speech is a central concern, as overly broad regulations risk chilling legitimate expression. Conversely, insufficient regulation can allow harmful content to proliferate, undermining public safety and social cohesion.
Legal Frameworks Governing Social Media Content and Free Speech
The legal landscape surrounding social media content and free speech varies considerably across nations. Many countries uphold a robust right to free expression, but this right is not absolute and is subject to limitations, particularly when it comes to content that incites violence, promotes hatred, or constitutes defamation. For instance, the United States employs a relatively high bar for restricting speech, adhering to the principle of “strict scrutiny” for content restrictions. This means that any limitations on free speech must be narrowly tailored to serve a compelling government interest. In contrast, some European countries have adopted stricter regulations, prioritizing the protection of individual dignity and preventing the spread of harmful content, even if it means imposing greater restrictions on free expression. This difference highlights the ongoing debate about the appropriate balance between free speech and the need to regulate harmful online content.
Comparative Approaches to Regulating Harmful Content
Different jurisdictions employ diverse strategies for managing harmful content on social media. Some favor a “reactive” approach, relying on user reporting and platform moderation to identify and remove problematic content after it has been posted. Others adopt a more “proactive” approach, using algorithms and artificial intelligence to detect and prevent the spread of harmful content before it reaches a wide audience. Furthermore, some governments mandate that social media platforms take down specific types of content, while others focus on imposing fines or other penalties for non-compliance with content moderation policies. The effectiveness of these different approaches is a subject of ongoing debate, with evidence suggesting that no single approach is universally superior. The effectiveness is often dependent on factors such as the specific type of harmful content, the resources available to platforms and regulators, and the cultural context.
Legal Challenges Related to Social Media Regulation
Numerous legal challenges have arisen concerning social media regulation, reflecting the complexities and ambiguities inherent in this area. These challenges often involve disputes over the interpretation of free speech protections, the scope of platform liability for user-generated content, and the effectiveness of government regulation. For example, several cases have challenged the legality of government mandates requiring social media platforms to remove specific types of content, arguing that such mandates violate free speech principles. Conversely, other cases have challenged platforms for failing to adequately moderate harmful content, arguing that they have a responsibility to protect users from harm. The outcomes of these legal challenges vary depending on the specific facts and legal context, but they collectively contribute to the ongoing evolution of the legal framework governing social media.
Social Media and Access to Justice
Social media platforms have fundamentally altered how individuals access information, connect with others, and engage in various aspects of life. This transformation extends significantly to the realm of law and access to justice, offering both unprecedented opportunities and considerable challenges. The speed and reach of social media can democratize legal information and resources, potentially bridging the gap between those who need legal assistance and those who can provide it. However, this potential is tempered by issues of digital literacy, misinformation, and the inherent complexities of navigating the legal system.
Social media can improve access to legal information and resources in several ways. Many legal aid organizations and government agencies utilize platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to disseminate information about legal rights, available services, and upcoming events. These platforms allow for targeted outreach to specific demographics or communities, ensuring that crucial information reaches those who might otherwise lack access. Furthermore, social media facilitates the sharing of legal documents, court announcements, and relevant news articles, making it easier for individuals to stay informed about developments in their cases or broader legal issues. Online forums and groups can also provide a space for individuals to connect with others facing similar legal challenges, offering peer support and shared knowledge. The increased visibility afforded by social media can also encourage pro bono legal services and incentivize lawyers to participate in public interest initiatives.
Potential Barriers to Accessing Justice Through Social Media
While social media offers considerable potential, significant barriers remain. Digital literacy is a critical factor; individuals without reliable internet access or the skills to navigate online platforms effectively are excluded from these benefits. The sheer volume of information available online can be overwhelming, making it difficult to identify credible sources of legal information amidst misinformation and misleading content. Privacy concerns are also paramount; sharing personal information online carries inherent risks, and individuals may be hesitant to seek legal help through social media due to concerns about data security. Finally, the uneven distribution of technology and digital literacy across different socioeconomic groups exacerbates existing inequalities in access to justice. Individuals in marginalized communities may face disproportionate challenges in leveraging social media for legal assistance.
Hypothetical Scenario Illustrating the Use of Social Media to Connect Individuals with Legal Aid Services
Imagine a single mother, Maria, who is facing eviction. She has limited resources and is unfamiliar with the legal process. Through a community Facebook group dedicated to supporting low-income families, she discovers a post by a local legal aid organization advertising free consultations. The post includes a link to the organization’s website, which provides detailed information about their services and eligibility requirements. Maria clicks the link, fills out an online intake form, and receives a confirmation email scheduling a virtual consultation via video chat. The ease of access, coupled with the familiarity of the social media platform, allows Maria to overcome the initial hurdles of seeking legal help and connect with the resources she desperately needs. This scenario highlights how social media can effectively bridge the gap between individuals seeking legal assistance and the organizations offering it.

Tim Redaksi